“], “filter”: { “nextExceptions”: “img, blockquote, div”, “nextContainsExceptions”: “img, blockquote, a.btn, a.o-button”} }”>
New perk! Get after it with native suggestions only for you. Uncover close by occasions, routes out your door, and hidden gems while you
>”,”title”:”in-content-cta”,”kind”:”hyperlink”}}”>join the Native Operating Drop.
Maximal oxygen uptake, or VO2 max, is maybe the one greatest predictor of long-term well being and longevity. It’s additionally the important thing trait that distinguishes elite endurance athletes. We all know all this from greater than a century of analysis… in males. Whether or not the identical issues maintain true for VO2 max in girls is much less clear, as a result of there merely isn’t as a lot information on them.
A brand new research from researchers on the Federal College of São Paulo in Brazil goals to fill a few of this hole. They recruited 85 runners and 62 sedentary individuals, all girls between the ages of 20 and 70, and cut up them additional into youthful (lower than 50) and older (larger than 50) age teams. Then they examined their VO2 max with a progressive treadmill take a look at to exhaustion, measured their physique composition with a DXA scan, and picked up details about their coaching and different health-related habits. The outcomes are printed (and free to learn) in Experimental Gerontology.
The headline findings are unsurprising: runners had increased VO2 max than non-runners, which means they had been capable of suck in, distribute to their muscle mass, and use extra oxygen per minute; youthful individuals had increased VO2 max than older individuals. However while you zoom in on the main points, some extra fascinating patterns emerge.
What the VO2 Max Information Reveals
There are 3 ways of expressing VO2 max. The primary is absolute VO2 max, which is solely the best quantity of oxygen you should use per minute, often expressed in liters per minute. Should you get fitter, you’ll be capable to ship and use oxygen extra shortly, enabling you to energy your train on sustainable cardio metabolism for longer. Conversely, when you get too unfit and your VO2 max drops too low, even easy every day actions like climbing the steps would require extra oxygen than you possibly can provide, turning them into difficult anaerobic efforts.
Right here’s how the absoluteVO2 max values in contrast for the 4 teams, with runners represented by circles and sedentary individuals by squares:
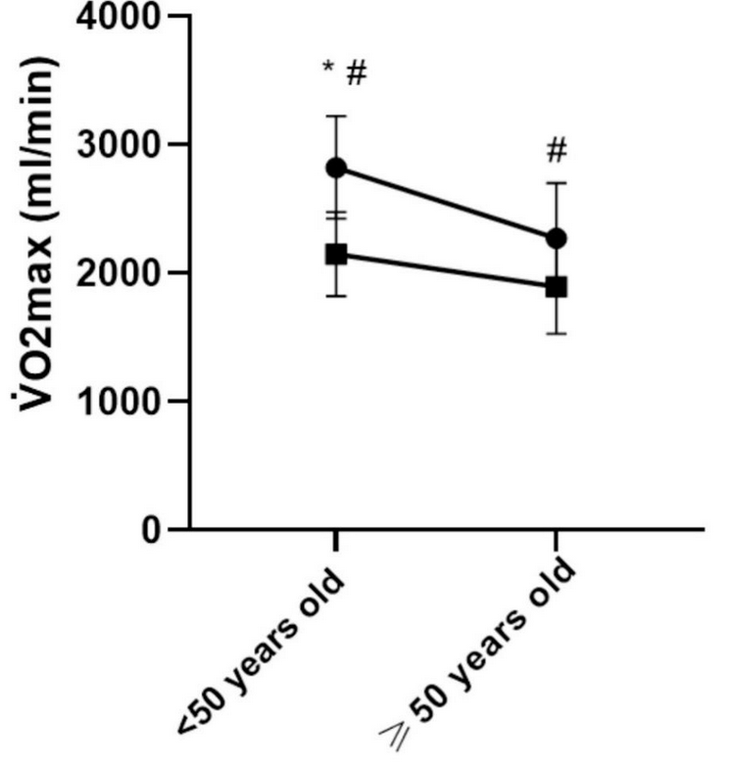
All which means that absolute VO2 max is a helpful marker of well being and efficiency—nevertheless it’s much less helpful for comparability between completely different individuals, as a result of the quantity of oxygen you utilize is dependent upon physique measurement. A heavyweight rower would possibly use twice as a lot oxygen as a diminutive marathoner, but when she’s twice as large then she’s not essentially fitter. As an alternative, she’ll want all that additional oxygen to maneuver her bigger physique round. A greater comparability can be to divide every particular person’s VO2 max by their weight, giving what’s referred to as relative VO2 max, expressed in milliliters of oxygen per kilogram of physique weight. Right here’s what that information appears like:
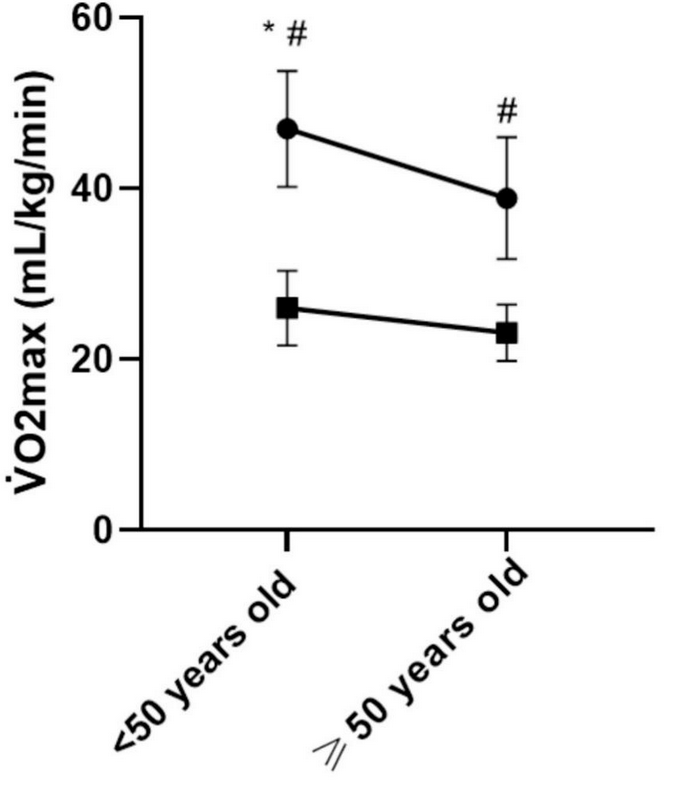
The important thing factor to note right here is that there’s a a lot greater hole between the runners and non-runners in relative VO2 max than in absolute VO2 max, which is as a result of the non-runners weigh considerably extra on common. The relative worth affords a a lot better reflection of how a lot fitter the runners are for working: what issues is not only how a lot cardio energy you possibly can ship, however how large a load that energy wants to maneuver.
Why Physique Composition Issues, Too
The researchers additionally current a less-common third approach of expressing VO2 max. On this case, they divided absolutely the worth not by complete weight, however by the burden of every particular person’s lean mass, which means primarily muscle in addition to connective tissue.
To grasp why that is related, it’s helpful to consider VO2 max by way of oxygen provide and demand. The normal view of VO2 max was that it was dictated by oxygen provide—that’s, by how shortly you can suck in oxygen, diffuse it out of your lungs to bloodstream, and pump it to your muscle mass. These are all thought of “central” limitations on VO2 max. The first approach altering VO2 max, on this image, is to your coronary heart to get stronger in order that it could pump extra blood to your muscle mass.
However oxygen demand additionally issues. It doesn’t matter how a lot oxygen you pump to your muscle mass in case your muscle mass aren’t able to extracting and, with the assistance of mitochondria, making use of it to supply cardio power. That’s why VO2 max is extra carefully proportional to your complete muscle mass than to your total weight. Should you add ten kilos of fats to your physique, your absolute VO2 max gained’t change as a result of fats doesn’t eat oxygen. Should you add ten kilos of muscle, your means to eat oxygen will improve, and your means to produce oxygen will probably observe go well with. How a lot muscle you could have, and the way successfully that muscle can use oxygen, are “peripheral” limitations on VO2 max.
Right here’s what the information confirmed for VO2 max divided by lean mass solely:
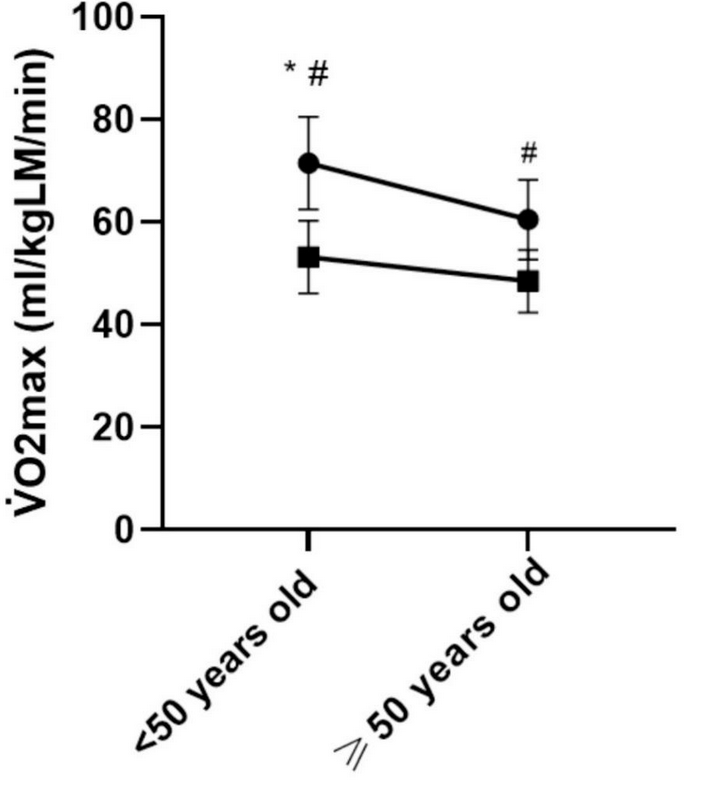
An Surprising Discovering About VO2 Max in Girls
Right here’s the place the shock is available in. Based mostly on earlier information from males, the researchers had hypothesized that these relative-to-muscle values can be much less affected by growing old than the relative-to-whole-body values. To place it one other approach, the male information had prompt that age-related declines in VO2max had been primarily associated to declines in central elements like the center and circulatory system, whereas peripheral elements like the flexibility of muscle to make use of oxygen stayed comparatively fixed. However that’s not what they discovered right here: each central and peripheral elements appeared to say no at comparable charges in girls.
Why ought to VO2-max declines in girls be completely different than in males? One chance is that it’s a fluke that’s particular to the comparatively small group of girls being examined right here. Nevertheless it’s additionally doable that there’s a real distinction. The researchers recommend that “intramuscular adipose tissue”—that’s, small quantities of fats positioned throughout the muscle itself, generally known as muscle fats infiltration—might play a job. This infiltration tends to be increased in girls, and will increase with age. If that’s what’s taking place, then it means that the mechanisms of VO2 max decline—and thus maybe one of the best countermeasures—are completely different in women and men.
There’s one closing level to notice on this information—one which, on this case, does echo earlier findings in males. The runners skilled a steeper VO2 max decline with age than the non-runners. This could be a kind of physiological regression to the imply: the upper you begin, the extra you’re prone to fall. Nevertheless it in all probability additionally displays the truth that older runners have a tendency to coach lower than youthful ones, a sample that confirmed up on this research too. There are many good causes for that, nevertheless it’s additionally a reminder: when you’re working onerous to be super-fit now, you’ll must preserve working equally onerous to be equally match sooner or later. In terms of health, saving for retirement solely takes you to this point.
For extra Sweat Science, be part of me on Threads and Fb, join the e-mail publication, and take a look at my guide Endure: Thoughts, Physique, and the Curiously Elastic Limits of Human Efficiency.










